Introduction
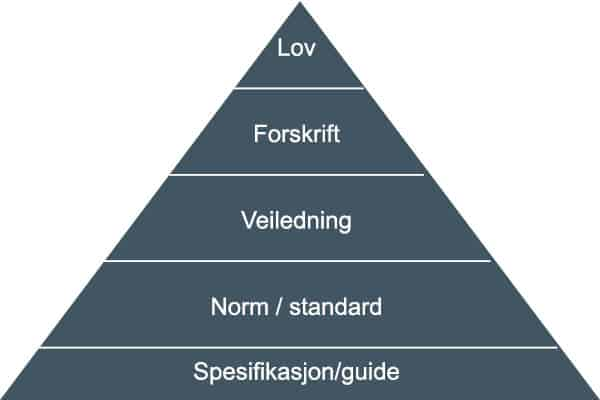
Laws are rules that give rights and obligations. In Norway, the Storting (parliament) makes the laws, and they come into force after adoption. Regulations belong to a law and provide more details. The ministry makes the regulations, which help to explain the law. In practice, regulations are used to find the rules that apply.
Norwegian maritime law has changed a lot since 1893, especially due to international agreements. These have led to requirements for safety equipment such as fire protection, navigation, rescue equipment and communication, as well as rules for operation, emergency measures, inspections, training and certificates.
All ships must be registered in a state and fly its flag. The ship must comply with the flag state’s laws and regulations. Although ships have no liability under international law, the flag state must follow international rules and has full authority over the ship. Maritime law, also known as admiralty law, governs the private law of shipping. Which laws apply is determined by the ship’s flag. For example, a ship flying the Liberian flag follows the laws of Liberia, also in Europe, including penalties for the crew.
Ship Safety Act – Chapter 4: Personal safety
The Ship Safety Act in Norway has a separate chapter on personal safety and working environment on board. This includes:
- § 28: Rules on safety representatives and working environment committees, which work for a safe working environment.
- § 29: The master’s duties to comply with the rules in this chapter, such as ensuring safety and well-being.
- § 30: Duties of everyone working on board, such as contributing to a good and safe environment.
- § 25: Requirements for living and leisure environments, so that seafarers have good living conditions and rest opportunities.
Flag states must ensure that the MLC rules are followed, so that the working environment on board is safe. The Ship Safety Act supports this with clear requirements for safety and welfare. “The Code of Safe Working Practices for Merchant Seafarers from the Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA) is a guide to health and safety on UK ships.
